Caching Strategies
I wanted to start writing blog for a long time let this be the first one. I have been looking into Microservice architecture for a while and i thought it would be nice to write while learning it. Today i will talk about Caching
1. Read Through
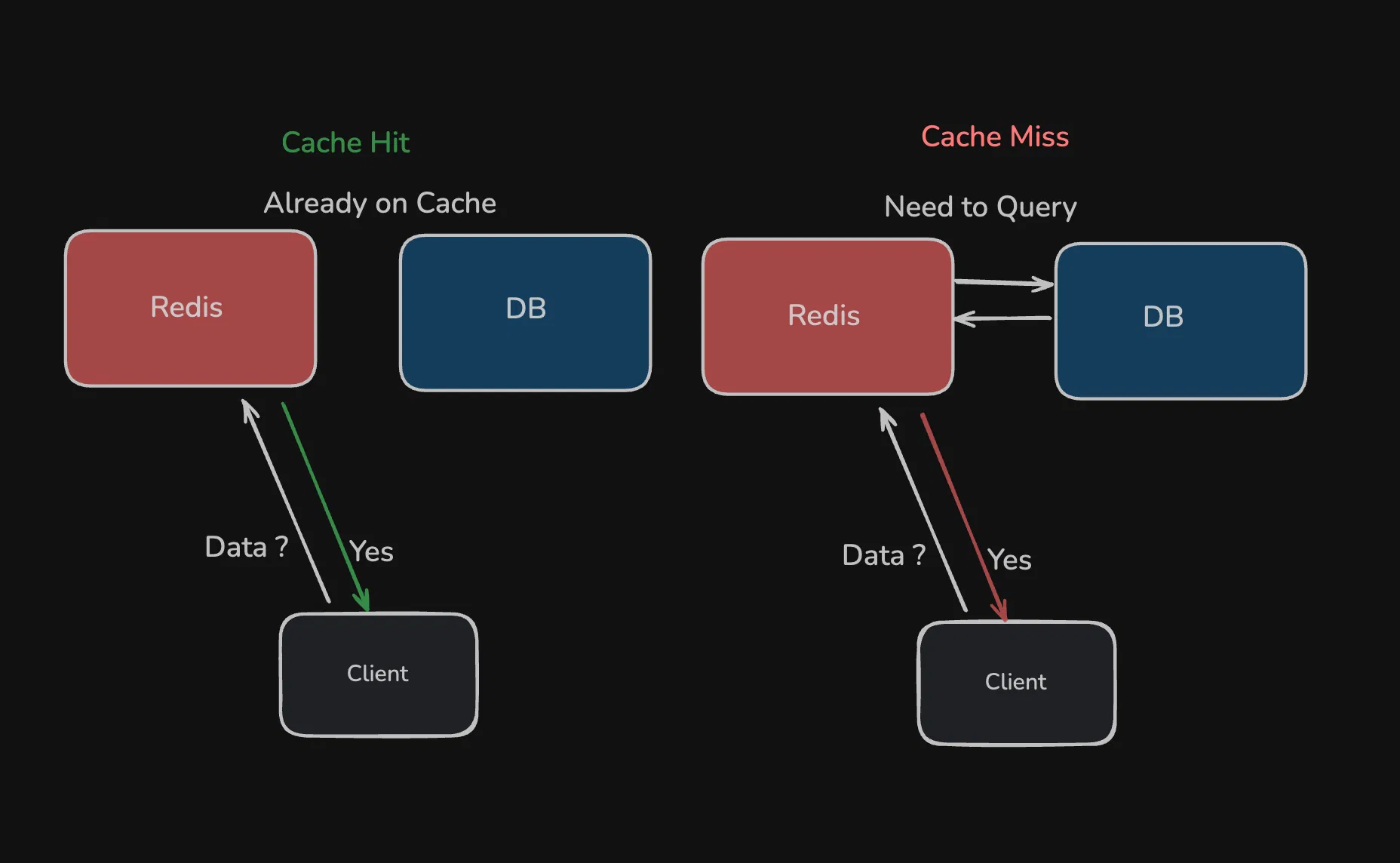
This is the one that comes up when i immediately explain about what caching is to someone Read Through caching is a strategy where your application when reqeust data it first look up the cache and if the data is available (cache hit) then the data is returned. Otherwise if the data is not available (cache miss) then the cache system itself is reposible to to fetch the data form DB and store it in the cache and return the data This approach simplifies application logic because the application does not need to handle the logic for fetching and updating the cache. As you can see the read operations for cache hit can be a bit slow. but for hits they are low-latency calls To prevent the data from being state we can use TTL(Time To Live) which will expire the data after the certain time
Read Through is best suited in places where data is read frequently but changes rarely and you are not highly concerned about data consistency this can offload the load from the database a lot
2. Write Through
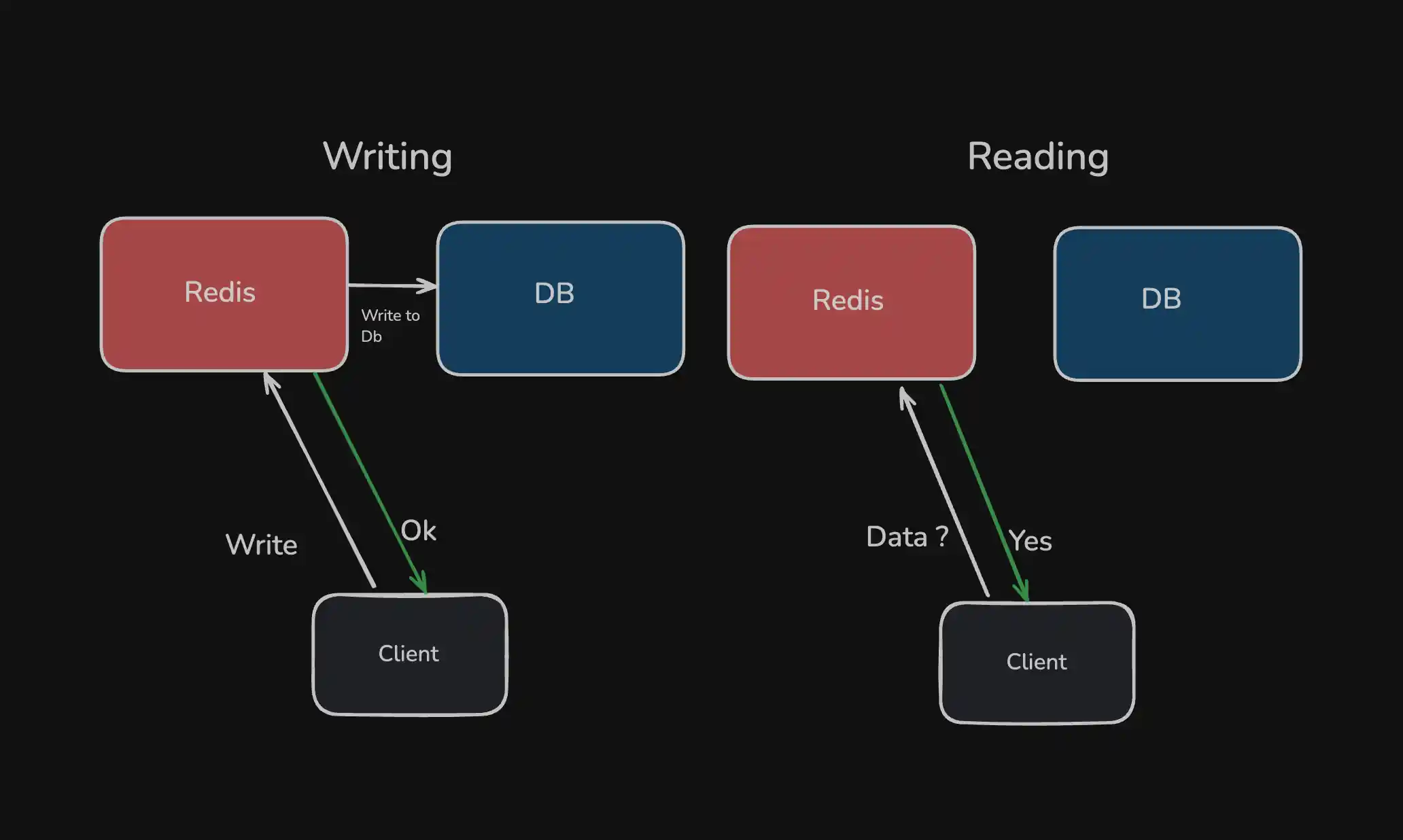
In Write Through strategy the write operation is done in a different way. When application writes some data it is written on both cache and on database, which ensures that the data is consistent across both systems. In other words
"Write to cache and write to the database — at the same time."
How read works
when data is read it is read from the cache system directly and here its always cache hit. We don't need to worry about data being stale because the write operation is done on both systems this ensures data consistency
Write Through can lead to slower writes and sometimes the all the cached data maynot be used and that is a waste of resource. Failure handling is another challenge here if the writing operation on cache or DB fails that leads to inconsistent state
when to use
- You need strong consistency between the cache and the database.
- Your application has frequent reads and regular writes.
- Read performance is critical and you want to avoid stale data.